5G
Joint call 5G Communication Technologies 2023
The Ministry of State, the Department of Media, Connectivity and Digital Policy, the Ministry of the Economy, the Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR) and Luxinnovation have joined forces to offer companies and research institutions a new funding opportunity that supports consortia to take advantage of 5G communication technologies.
Starting date
15 November 2023
Application deadline before
09 February 2024
Context of the call
5G communication technologies have the potential to be seen as an accelerator for many applications. For home users, 5G will make it much faster to download content, such as being able to download a 2-hour movie in less than 10 seconds, compared to 7 minutes with 4G. In major industries, 5G is expected to alter the way services are delivered in the future. For example, smart environments, smart cities, and Industry 4.0 are particularly well-positioned to take advantage of the benefits offered by 5G communication technologies. An IoT-enabled sensor technology used in the farms to monitor soil moisture improves yields while reducing water use. By using 5G, which could deliver a significantly faster data rate, the traffic flow can be improved, and hence more accurate traffic information can be provided. Industry 4.0 applications will lead to flexible production line alignment and enable production quantities at lower production costs. While some of the applications of 5G are already known, many more new services and applications are expected to be developed as coverage becomes more widespread – the same way smartphones led to the creation of new apps and services.According to the European Commission’s plan “5G for Europe Action Plan” the main target was to make 5G commercially available in at least one major city in every Member state and pave the way for the so-called ‘Gigabit society’ through 2025, when all urban areas, major roads, and railways, are expected to have uninterrupted 5G coverage. But availability should not remain the main achievement, focus should be drawn to the take-up of products, services, and systems as well, taking into account the new technologies and providing solutions for various fields of applications.
The 5G strategy for Luxembourg launched by the Government is focused on the successful transition of existing communication technologies to 5G and comparable technologies. To emphasize the significance of a successful transition, the SMC conducted two proof-of-concept research grant calls. The projects co-funded in the frame of these two calls yielded promising results. The lesson learned from these calls further demanded a need that could further leverage the potential of 5G for the benefit of the research organizations (public, private, and public administrations) in Luxembourg. This further enables all said parties to explore new research directions while making use of 5G communication technologies.
To address this, the Ministry of State, the Department of Media, Connectivity and Digital Policy, the Ministry of the Economy, the Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR), and Luxinnovation are launching a joint call for research proposals aimed at encouraging close and interactive collaborations between private companies and public research institutes to carry out innovative research projects on 5G communication technologies. It is a strategic priority of the FNR to turn public research into a competitive advantage for Luxembourg and to open opportunities for researchers to sustain a high-impact research strategy while engaging with the most innovative private actors. To this end, the FNR supports the advancement of Luxembourg's knowledge-based economy by supporting applied research, by reinforcing cooperation between public research and innovative economy, and by facilitating the potential commercial exploitation of research results.
Purpose of the call
5G communication technologies have the potential to be a crucial enabler in various areas such as Smart Environment, Smart Cities, and Industry 4.0. Solutions to these areas are still not readily available. The topology of the communication network will largely depend on the application type. For example, the smart environment solutions may prioritize long-range functionalities as compared to Industry 4.0 applications will need to incorporate low-latency functionalities. It is within these technical boundaries that the development of innovative and inventive projects shall take place. Promoting digitalization through the development and validation of innovative 5G-based communication solutions will enable Luxembourg’s economy to become a leading player in the global 5G communication technology market.Objectives
New opportunities for companies can be created by the use of 5G-based applications and communication systems. To be effective in the communication and network topology strategy, the network topology strategy requires cutting-edge technologies that match the latest scientific and technical advances in the field. In order to leverage the applications and the existing communication systems, 5G communication technology is instrumental and represents a key element in building a sustainable, competitive, and digital economy in Luxembourg.In that sense, the joint call for projects aims at facilitating collaborative projects between public research institutions and companies to jointly achieve applied research and development results that are mutually beneficial. Public research institutions will have the opportunity to address new or different research questions, and companies can improve their innovation capabilities and gain access to the latest trends in the field of 5G-based applications and communication systems. It is important for projects to contribute to the national industrial and economic landscape and align with national strategic priorities.
The specific objectives of the joint call on 5G communication technologies are:
- to support innovation and sustainable value creation by stimulating strong partnerships between public research institutes and companies in the field of 5G communication technologies.
- to increase the company’s expertise in 5G communication technologies applications in order to enhance their use of complex data transmission in areas such as IoT, edge computing, and artificial intelligence.
- to encourage the implementation of innovative projects that contribute to the development of Luxembourg's industrial and economic landscape and are in line with national strategic priorities.
- to increase the attractiveness of Luxembourg as an innovation hub based on advanced technological research on 5G communication technologies.
The individual objectives to which the projects shall contribute can be summarized as follows:
- to test the provision of innovative and reliable services over 5G in terms of coverage, capacity, latency, and quality of service. (generating knowledge)
- to gain experience with the operation of 5G networks and the implementation of 5G-driven services that facilitate the identification of any obstacles or bottlenecks, and research and testing of appropriate solutions. (generating and integrating knowledge)
- to test innovative applications using technologies that can be substitutes and/or complements to 5G, such as satellite communication systems or similar technologies. (generating knowledge)
Call topics
The projects to be carried out within the framework of this call must be innovative, of the highest quality, and contribute to the development of Luxembourg’s industrial and economic landscape. The projects must have a positive and sustainable impact on diversifying or strengthening the companies' future business activities and contribute to the development of business opportunities via expanding the network, and the knowledge transfer. Projects may be in the field of industrial research[1] and/or experimental development[2]The research and development projects must address innovative problems that require 5G communication resources. Applications must clearly state why the work requires access to a 5G communication system. The innovative 5G communication technology-based solutions that will be developed during this call are anticipated to be innovative and allow the Luxembourg economy to become more competitive and sustainable by capitalizing on the innovative integration of 5G communication technology. The joint call focuses on 4 important topics:
1.Smart Environment
Smart environment targets the development and validation of 5G technology-based applications for monitoring and reacting to the status of the environment.
2.Smart Cities
Smart cities topic targets the development and implementation of 5G technology-based solutions to improve the efficiency, security, sustainability, and management of the urban environment.
3.Industry 4.0Industry 4.0 is among others transforming manufacturing and production processes including warehouse management and logistics through the extensive use of data, digitalization, and automation.
4.Technologies
The technologies topic targets the definition and development of innovative components and optimized network topologies to go beyond normalized 5G telecommunications networks.
The following examples could provide some inspiration (mainly for guidance) to the project consortium.
Resources are finite and will soon become increasingly valuable. While using the latest 5G technologies, a potential surveillance system could help to better understand resource flows and provide alternatives for better management of these resources. When it comes to water and energy use, the first idea would be to reprimand energy needs. What can be done, especially in telecommunications networks to optimize the system's performance, thus reducing the need for energy? While it is not a typical telecommunications project, there is a clear research note. The main milestones of this project are the first stage of the condition analysis and the second stage of the development of the required algorithms. The last step would then be to validate the algorithm demonstrating a potential result. The same approach can be applied to non-technical applications such as farming optimization. On-site measurement data collection by means of 5G communication technologies in combination with alternative data sources could potentially lead to improved resource management that improves yield. Another very important topic is the fast response to extreme meteorological weather conditions. By means of a modern and flexible communication network, we could be able to collect data directly from the source and thus take the appropriate actions in order to avoid unnecessary damage and provide accurate warning information.
As far as transportation is concerned, 5G networks will play a major role in the future. It is about transporting a considerable amount of data at the lowest latency possible to a multitude of connection partners. To some extent, this application has roots in resource management. How can we optimize our traffic flow? What information do we provide in order to maximize our peers? Some initiatives to address these issues are already emerging; the concept of a digital twin is on its validation path. Nevertheless, transport is not only about the flow of information but also about using applications in machine learning algorithms. Update in real-time relevant traffic information and provide alternative routing information while utilizing machine-learning elements. All these efforts may lead as well to autonomous driving applications. Another less dynamic but still important topic is the shipment and tracking of transport goods. Where is the shipment now and when will it be at disposal in a specific location? A major challenge is the management of a construction site. What is the actual status of the in-situ equipment? Which deliveries are expected? What can be done to reduce shipments to the site? Using IoT (Internet of Things) technologies with a 5G communication network, collecting the necessary data, and communicating the actual condition to outside delivery points should increase the efficiency of construction site management. Create real-time inventories and develop algorithms for optimizing on-time delivery, delivering data for flexible process management.
An old production line is based on a cabled concept, which makes it not always possible to operate the lines in a flexible manner. The industry 4.0 approach encourages the production line to be more flexible for products that are highly specific. The use of a private wireless communication system would enable the design and operation of this production line to be very flexible. This will again enhance market responsiveness. Private Industrial Network solutions have the potential to be a crucial solution. The huge quantity of data gained in an IOT network does not necessarily need to be transported to a centralized processing infrastructure. The idea is to create a decentralized data and machine-learning unit at the data source points. By doing this, the network load can be reduced, throughput speed can be increased, and the single point of failure can be eliminated.
5G telecommunications networks as they stand today are normalized. The challenges that await us will consist in identifying the perfect components. Whether you need low latency, high data processing rates, or target data processing, this is an exercise to figure out the best possible network topology. The newly introduced AAS antennae do play an important role in what goes with efficiency. Parameters related to antenna configuration and adherence to regulatory thresholds are the key elements to define better algorithms for optimized radio networks. Satellite coverage is less complicated than using a land-based communication network. A possible scenario could be to make 5G technology available in areas where no terrestrial communication is possible due to a lack of infrastructure using satellite communication support. At its best, this would potentially reduce the number of base stations while maintaining the highest network quality.
General eligibility criteria and instruments of the joint call
1. Consortia are expected to include at least one eligible participating company and one FNR-eligible participating public research organization. In the consortium, the contribution of the private and public parties should be as close to equal as possible, whereas o party shall bear more than 70% of the total project cost. Companies must fulfil the general eligibility criteria of article 2 of the RDI law [1] and the respective criteria of the specific State aid scheme they apply for as set out in the R&D schemes [2]. Research organizations must be eligible under article 3-(2) of the FNR statute (Loi modifiée du 31 mai 1999 portant création d'un fonds national de la recherche dans le secteur public) and be registered at the FNR.2. The project must be in the field of industrial research1 and/or experimental development2 as defined in article 1 of the RDI law [1], and in line with the call topic.
3. For research and development activities under the joint call for projects, public institutions should comply with the general principles set forth in the FNR Guidelines, such as the formal requirements to qualify as PI (Principal Investigator) of an FNR-funded project and/or as supervisor of an FNR-funded Ph.D. student, the FNR Research Integrity Guidelines, and the FNR data management plan, as well as those included in the FNR BRIDGES Programme description.
The FNR will fund the costs of the eligible public research organizations in Luxembourg, up to 700.000 € per project covering all project-specific costs.
The Ministry of the Economy will co-finance costs borne by Luxembourg-eligible companies up to 700.000 € per project, using the R&D aid scheme [1].
It is expected that the projects will be considered either as industrial research and/or experimental development projects. In this case, the maximum co-financing rates for companies through collaboration are as follows:
| Maximum aid intensities | Large company | Medium company | Small company |
| Experimental development | 40% | 50% | 60% |
| Industrial research | 65% | 75% | 80% |
The costs related to patents and certifications are not eligible in this call. However, for SMEs (large companies excluded) these costs can be co-funded up to 50% under the Innovation Aid for SMEs aid scheme [4]. In this case, the SME has to file a separate State aid request to the Ministry of the Economy.
The project duration is a maximum of 36 months continuous period.
For public research organizations, FNR financial regulations apply.
Self-funded international or national partners are permitted to participate in the consortium.
Evaluation criteria and scoring system of the joint call
The project proposals will be evaluated in a balanced manner based on the following criteria and considering the general considerations formulated under the call topic and objectives:1.Relevance (33.33%)
This criterion aims to evaluate the quality and the innovative character of the project through the following aspects:
- project idea, clarity, and pertinence of the objectives.
- level of innovation, including advancements on the state-of-the-art.
- soundness of the research approach and methodology.
- scientific and technical maturity of the project.
- clarity, coherence, and adequacy of the application regarding the theoretical framework, objectives, methodology, work plan, and expected results and impacts.
- pertinence/level of 5G technologies.
This criterion is intended to assess the quality and feasibility of the project work plan to ensure its success. The following aspects are taken into consideration:
- coherence and effectiveness of the work plan, including appropriateness of the allocation of tasks and resources.
- competencies, experience, and complementarity of the individual participants, as well as of the consortium and collaboration as a whole.
- the level of ambition of the collaboration and commitment of the participants in the proposed program.
- appropriateness of the management structures and procedures, quality of the risk management plan, and soundness of the risk mitigation plan.
- development processes shall be based on “security by design” principles in order to reduce the risk of cyber threats.
This criterion is intended to assess the potential impacts and contributions of the project. The following aspects are taken into consideration:
- economic and societal added value of the proposed research and development project in line with national priorities.
- strengthening the competitiveness and growth of involved companies and research organizations by developing innovations.
- contribution of the project to the advancement of knowledge and expertise of companies in the field of 5G communication technologies such as IoT design and operation, edge computing and real-time processing.
- effectiveness of the proposed measures to exploit and disseminate the results of the project.
- particular focus on R&D projects involving new innovations and processes rather than improvements to existing technologies and core business activities.
- where applicable, the soundness of the business plan outlining a clear path towards an economic exploitation of the project results, and to what extent can the project carry on beyond the co-funding period.
Call process
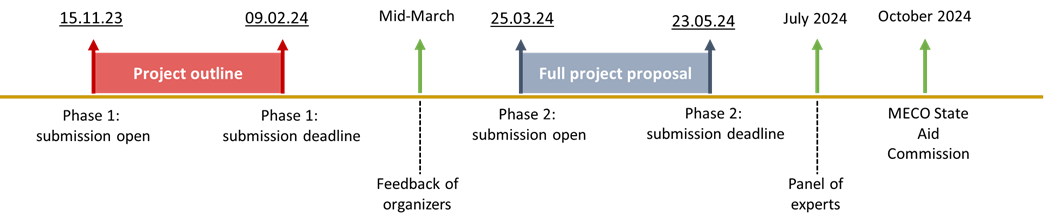
The submission and evaluation process will be composed of 2 phases.1.Submission process
Phase-1: (15th of November 2023 9am - 9th of February 2024 2pm)
Project outline (PO) to be submitted on the research-industry-collaboration platform of Luxinnovation. The PO shall provide information on:
- Project description;
- Project outcomes;
- Expected technical contributions of the different partners;
- Estimation of 5G communication technologies systems resources;
- Statement explaining the benefits of using 5G-based communication technologies;
- Intellectual Property Rights for collaborative project proposals (in view of a draft collaboration agreement in phase 2);
- Preliminary project costs;
- CV of the main investigators;
- For companies: Organizational chart of the group, 2021 and 2022 balance sheets and P&L accounts of the applicant and the group, cash-flow forecast.
Full project proposal (FPP) to be submitted by each project participant to the Ministry of the Economy (Myguichet platform) for companies and to FNR (FNR Grant system) for accredited research organizations. The models of FPP as well as the financial annexes to be appended by each partner to the aid application can be downloaded from the platform www.research-industry-collaboration.lu.
The FPP shall provide information on:
- Detailed description of the research project;
- Different activities of the project (Work packages);
- Description of the technical challenges and implementation of the project;
- Description of the expected outcome and the economic impact;
- Milestones;
- Timeline;
- Resources;
- Description of costs;
- Collaboration agreement (draft ready for signature) including agreement on intellectual property[3];
- GDPR aspects: data flow and ownership, delegations to data processors.
Phase-1:
Based on the Project Outlines (PO) and the annexes submitted via the research-industry-collaboration platform, the granting authorities in collaboration with Luxinnovation will check:
- Eligibility of all parties and co-funding capacity of the company;
- If the project description is in line with the call topic;
- If the technical capabilities and benefits of using 5G based communication and application technologies are consistent with the topic and the objectives of the call.
Participants will obtain written feedback from the granting authorities on Luxinnovation’s research-industry-collaboration platform. In case of a high number of POs, the granting authorities reserve the right to make a pre-selection based on the budget of the joint call, the level of innovation and quality of the application, as well as the economic and societal impact in line with national strategic priorities. In case of a positive pre-evaluation, applicants will be invited to proceed to Phase-2, possibly with some recommendations from the organizers of the call.
Phase-2:
Full project proposals (FPP) prepared in Phase-2 will be reviewed by an independent expert panel (“panel”) that will assess FPPs from a scientific/technical and economic point of view. The panel will establish a ranking list based on the criteria set in the “Evaluation criteria and scoring system” section above. The highest ranked projects will be recommended for funding to FNR and the Ministry of the Economy. In the case of companies, all projects will need to undergo an additional consultation at the State Aid Commission. The decision on the company’s grant is subject to a further positive recommendation by the State Aid Commission.
A project can only be funded by a concurring decision of FNR, the Ministry of State, the Department of Media, Connectivity and Digital Policy and the Ministry of the Economy.
The results of the evaluation will be communicated in October 2024. Projects are expected to start in November 2024.
Joint Call 5G Communication Technologies timeline
References:
[1] Modified law of May 17, 2017, on the promotion of research, development and innovation.
[2] https://guichet.public.lu/en/entreprises/financement-aides/aides-recherche-developpement/rdi/aides-rdi.html
[3] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52014XC0627(01)&from=EN
[4] https://guichet.public.lu/en/entreprises/financement-aides/aides-recherche-developpement/rdi/aide-innovation-pme.html
[2] https://guichet.public.lu/en/entreprises/financement-aides/aides-recherche-developpement/rdi/aides-rdi.html
[3] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52014XC0627(01)&from=EN
[4] https://guichet.public.lu/en/entreprises/financement-aides/aides-recherche-developpement/rdi/aide-innovation-pme.html
[1] ‘industrial research’ means the planned research or critical investigation aimed at the acquisition of new knowledge and skills for developing new products, processes or services or for bringing about a significant improvement in existing products, processes or services. It comprises the creation of components parts of complex systems, and may include the construction of prototypes in a laboratory environment or in an environment with simulated interfaces to existing systems as well as of pilot lines, when necessary for the industrial research and notably for generic technology validation.
[2] ‘experimental development’ means the acquisition, combination, shaping, and use of existing scientific, technological, business, and other relevant knowledge and skills with the aim of developing new or improved products, processes, or services. This may also include, for example, activities aiming at the conceptual definition, planning, and documentation of new products, processes, or services.
[3] Any intellectual property (IP) rights that result from the collaboration should be allocated to the different collaboration partners in a manner which adequately reflects their contributions and respective interests in the project. The main IP terms of the collaboration agreement between the company and the public research institute should thereby comply with the “Framework for State aid for research and development and innovation (2014/C 198/01)”, paragraph 2.2.2. “Collaborations with undertakings” [3].
